A VERY BIG DEAL report which has supported a hypothesis that the common cold has assisted in building immunity and it’s the T cells not the antibodies will likely be the key. Those who live in ultraclean environment less likely to by asymptomatic and will develop a more severe response to SARS-CoV-2 – the virus that causes covid-19. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-020-00808-x?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social&utm_content=organic&utm_campaign=NGMT_USG_JC01_GL_NRJournals
“SARS-CoV-2-specific peptides enabled detection of post-infectious T cell immunity, even in seronegative convalescent individuals. Cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2 peptides revealed pre-existing T cell responses in 81% of unexposed individuals and validated similarity with common cold coronaviruses, providing a functional basis for heterologous immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diversity of SARS-CoV-2 T cell responses was associated with mild symptoms of COVID-19, providing evidence that immunity requires recognition of multiple epitopes. Together, the proposed SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes enable identification of heterologous and post-infectious T cell immunity and facilitate development of diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic measures for COVID-19.”
“Knowledge obtained from the two other zoonotic coronaviruses SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV indicates that coronavirus-specific T cell immunity is an important determinant for recovery and long-term protection12,13,14,15. This T cell-mediated immune response is even more important as studies on humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-1 provided evidence that antibody responses are short-lived and can even cause or aggravate virus-associated lung pathology”
“Alignments of the SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes recognized by unexposed individuals revealed similarities to the four seasonal human common cold coronaviruses (HCoV-OC43, HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1) with regard to amino acid sequences, physiochemical and/or HLA-binding properties for 14 of 20 (70%) of the epitopes, thereby providing clear evidence for SARS-CoV-2 T cell cross-reactivity (Fig. 5b, Supplementary Tables 10 and 11 and Supplementary Data 1). Together, cross-reactive T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 HLA class I and HLA-DR T cell epitopes were identified in unexposed individuals. These cross-reactive peptides showed similarity to common cold coronaviruses, providing functional basis for heterologous immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection. ”
“Of the SARS donors, 100% showed T cell responses to cross-reactive and/or specific ECs (HLA class I 86%, HLA-DR 100%; Fig. 5d,e), whereas 81% of PRE donors showed HLA class I (16%) and/or HLA-DR (77%) T cell responses to cross-reactive ECs”
“SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes enabled detection of post-infectious T cell immunity in 100% of individuals convalescing from COVID-19 and revealed pre-existing T cell responses in 81% of unexposed individuals.”
“SARS-CoV-2-specific peptides enable the detection of post-infectious T cell responses, even in seronegative convalescents.”
So the below statement is very important – regardless of age and other variables sex, age, BMI did not correlated well with severity other than the diversity of T cell response to SARS-CoV 2!
“Alike in critically ill patients27, independently of age: high-antibody ratios were significantly associated with disease severity in our collection of convalescent SARS donors (n = 180, group 1 and 2), who in general were in good health and had not been hospitalized (Fig. 6f and Extended Data Fig. 5a). Neither the intensity of SARS-CoV-2-specific nor of cross-reactive T cell responses to HLA class I or HLA-DR ECs correlated with demographics (sex, age or body mass index; Supplementary Tables 12 and 13) or disease severity (Fig. 6g). Rather, diversity of T cell responses in terms of recognition rate of SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes (number of recognized epitopes normalized to the total number of tested epitopes in the respective donor) was decreased in patients with more severe COVID-19 symptoms (Fig. 6h and Extended Data Fig. 5b), providing evidence that development of protective immunity requires recognition of multiple SARS-CoV-2 epitopes.”
“determination of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 relies on the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses. However, despite the high sensitivity reported for several assays there is still a substantial percentage of patients with negative or borderline antibody responses and thus unclear immunity status after SARS-CoV-2 infection28. Our SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell epitopes, which are not recognized by T cells of unexposed donors, allowed for detection of specific T cell responses even in donors without antibody responses, thereby providing evidence for T cell immunity upon infection. In additional analyses of T cell immunity in hospitalized donors, we could prove SARS-CoV-2 T cell responses also in severely ill patients with COVID-19.”
“Using predicted or random SARS-CoV-2-derived peptide pools, very recent studies reported pre-existing SARS-CoV-2-directed T cell responses in small groups of unexposed as well as individuals who are seronegative for SARS-CoV-2, thereby suggesting cross-reactivity between human common cold coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 (refs. 18,19,20). In our study we identified and characterized the exact T cell epitopes that govern SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactivity and proved similarity to human common cold coronaviruses regarding individual peptide sequences, physiochemical and HLA-binding properties38,39. Notably, we detected SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells in 81% of unexposed individuals after a 12-d pre-stimulation. Furthermore, evidence was provided for a lower recognition frequency of cross-reactive HLA-DR EC in hospitalized patients compared to donors with mild COVID-19 course, which might suggest a lack of pre-existing SARS-CoV-2 T cells in severely ill patients”
“The pathophysiological involvement of the immune response in the course of COVID-19 is a matter of intense debate. We showed a correlation of high antibody titers with enhanced COVID-19 symptoms in our cohort of nonhospitalized patients. This finding is in line with recent data describing a correlation of high antibody titers with disease severity in hospitalized patients27. Our data together with a recently published study20 provide evidence that, on the other hand, the intensity of T cell responses does not correlate with disease severity. This finding is of high relevance for the design of vaccines, as it provides evidence that disease-aggravating effects might not hamper the development of prophylactic and therapeutic vaccination approaches aiming to induce SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell responses. In contrast to the intensity of the T cell response, we showed that recognition rates of SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes by individual donors were lower in individuals with more severe COVID-19 symptoms. This observation, together with our data on increased T cell epitope recognition rates after SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to pre-existing T cell responses in unexposed individuals and reports from other active or chronic viral infections associating diversity of T cell response with antiviral defense45,46,47, provides evidence that natural development and vaccine-based induction of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 requires recognition of multiple SARS-CoV-2 epitopes”
“our data underline the high importance of the identified T cell epitopes for further studies of SARS-CoV-2 immunity, but also for the development of preventive and therapeutic COVID-19 measures. Using the SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes we are currently preparing two clinical studies (EudraCT 2020-002502-75; EudraCT 2020-002519-23) to evaluate a multi-peptide vaccine for induction of broad T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2 to combat COVID-19.”
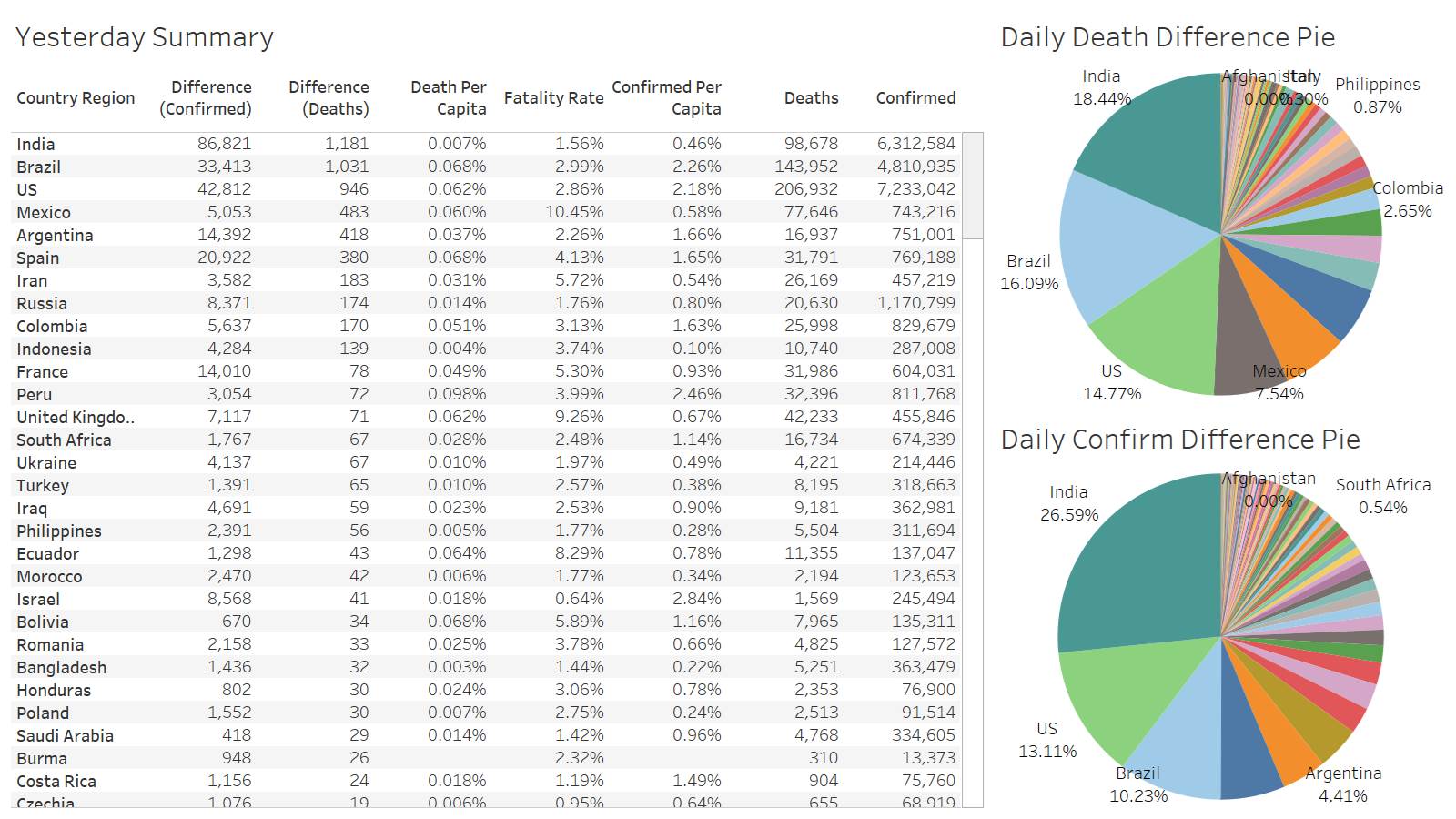
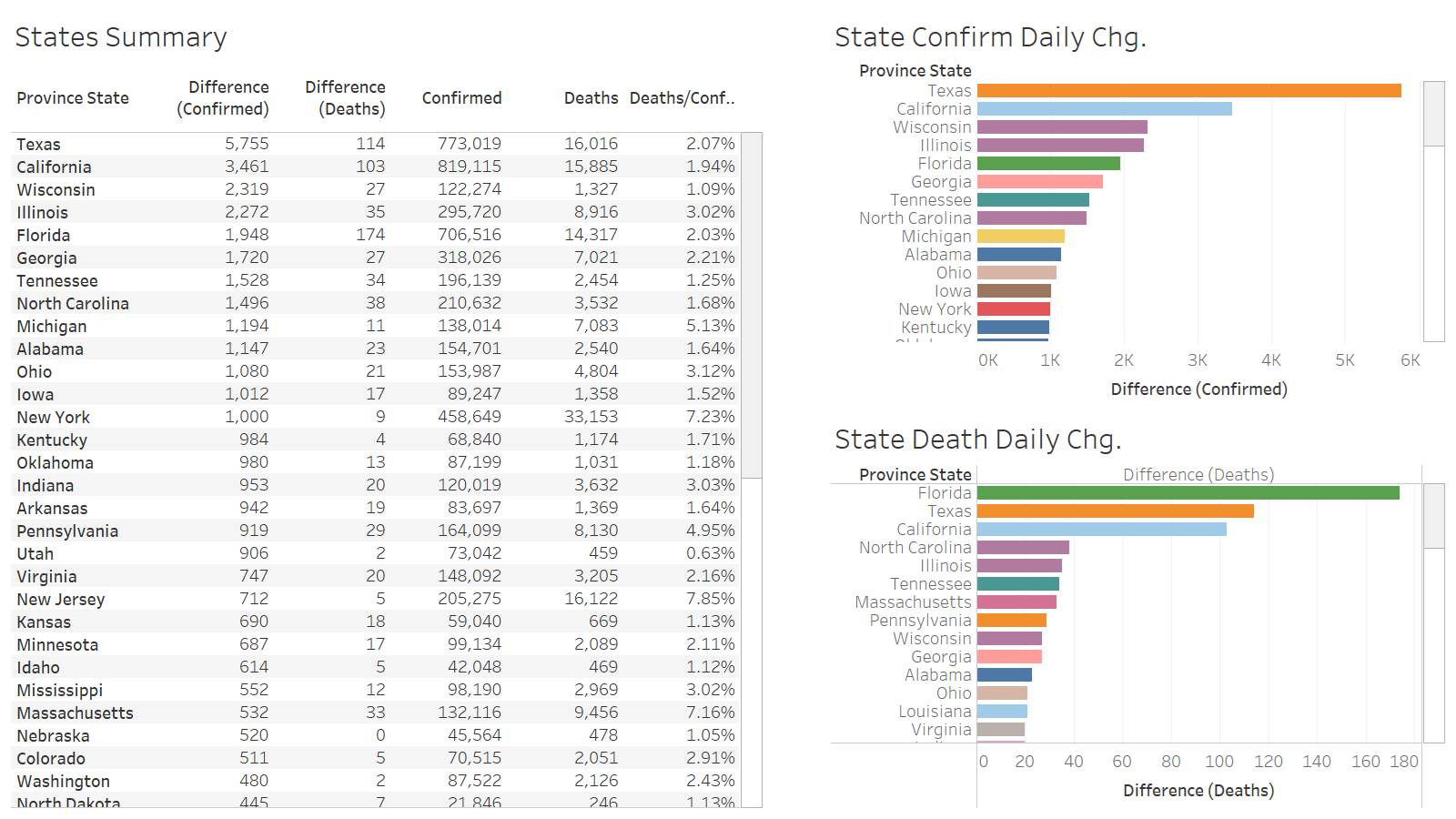
US below 1K deaths again and in the middle of the week!
Fl leading the way at 174 for the US
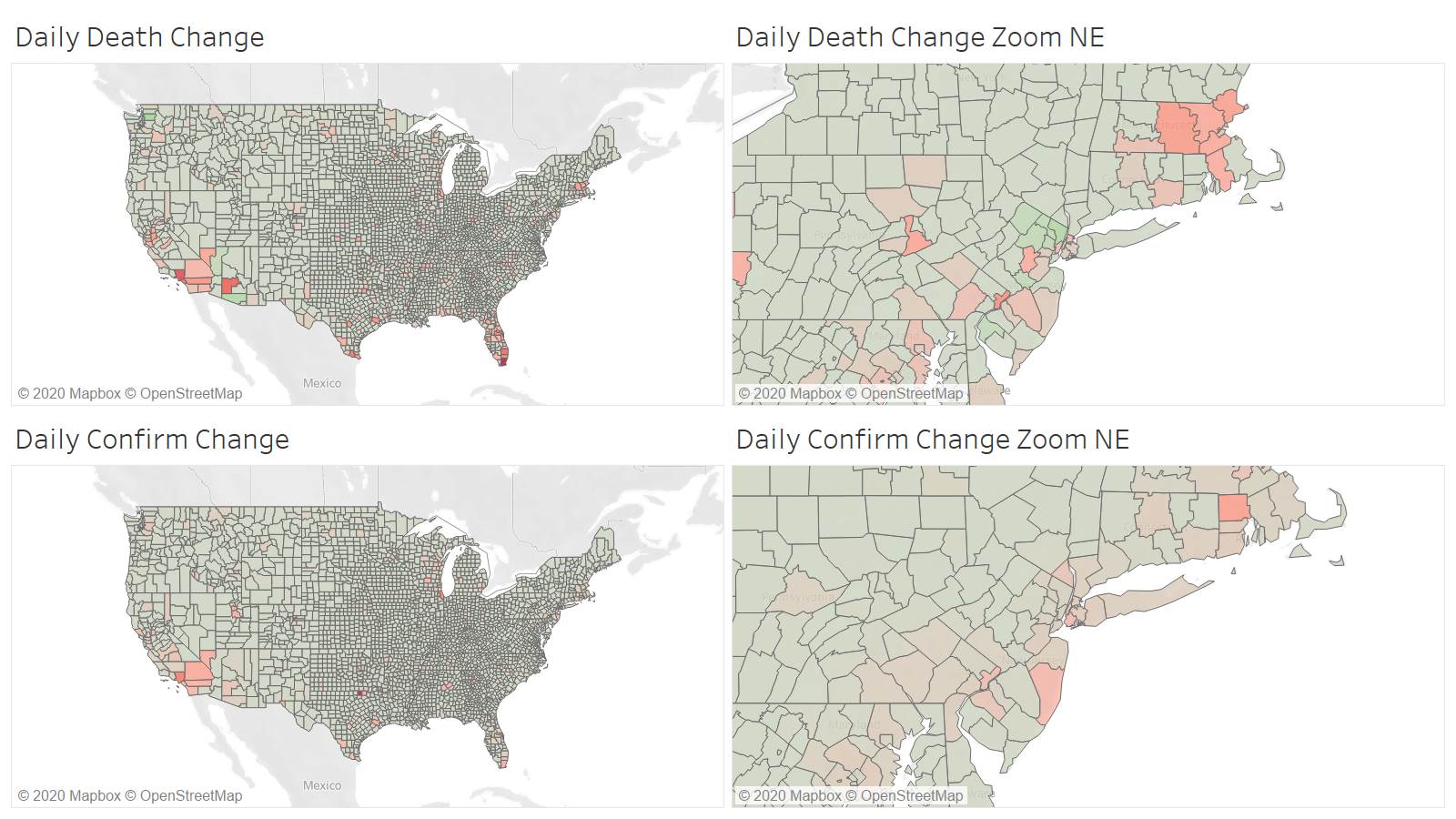
Once again Miami-Dade leading all counties at 37.
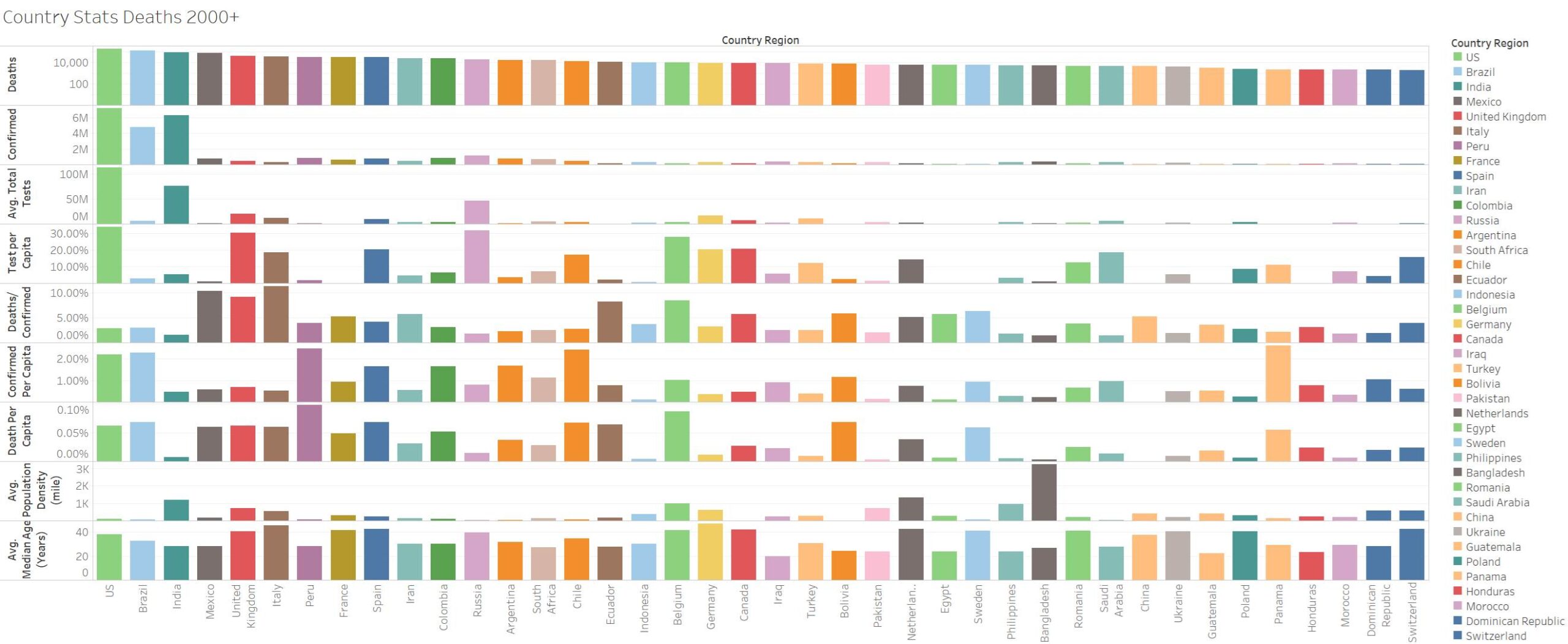
I had to change the chart from 1000+ to 2000+ in order to reduce the amount of countries to a readable amount